Spray drying is rapidly becoming one of the most transformative technologies in the pharmaceutical industry. This continuous process efficiently converts liquid feeds into powders with precise attributes, such as particle size, morphology, and stability—key factors for pharmaceutical formulations. Let’s dive into how spray drying is revolutionizing drug production and how advancements in this technology are enhancing process development.
What is Spray Drying?
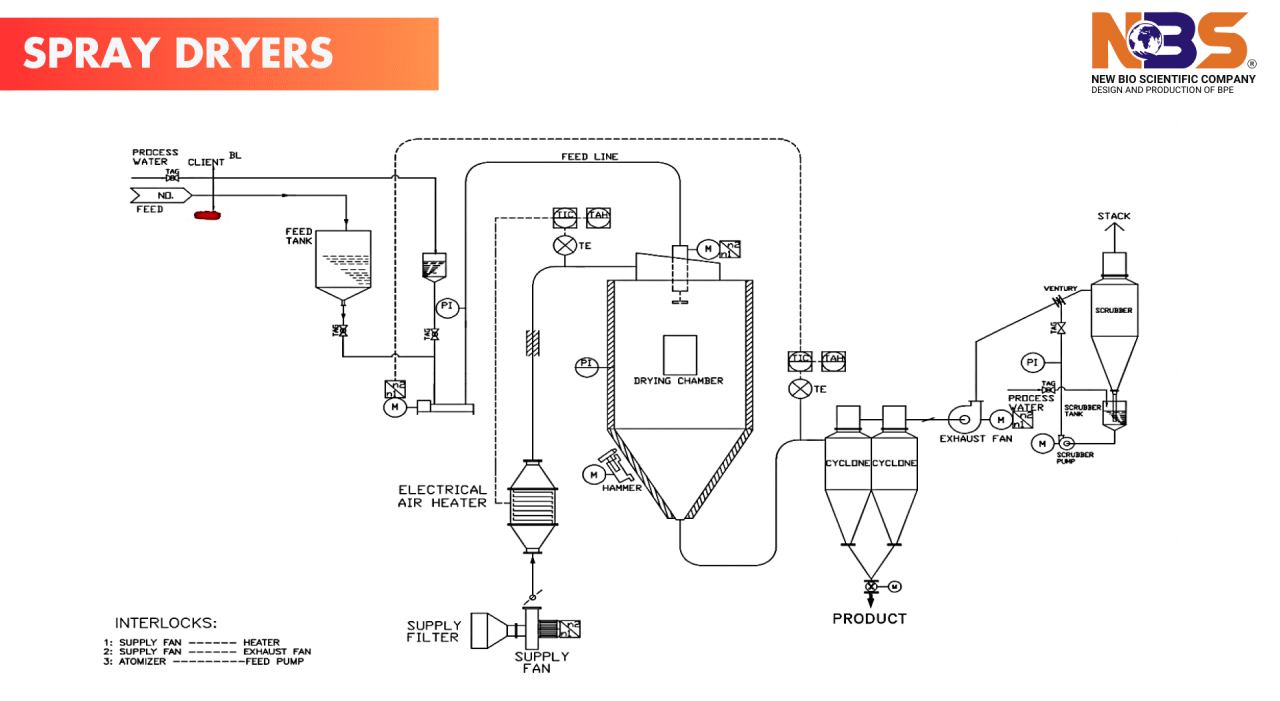
Spray drying is a drying technique that transforms a liquid feed into a dry powder in a single step. The process involves atomizing a liquid into tiny droplets and exposing them to hot drying gases, causing rapid evaporation and turning the liquid into solid particles. These particles are then separated from the drying gas through cyclones and filters. The result is a powder or granules with highly defined properties.
Though spray drying was first conceptualized over 140 years ago, its industrial applications only became widespread in the 20th century, with milk powder production being its first major success. Today, it is used in diverse industries such as cosmetics, fine chemicals, polymers, and, of course, pharmaceuticals.
Why is Spray Drying Important for Pharmaceuticals?
In pharmaceutical manufacturing, precise control over powder properties is essential, and spray drying offers flexibility like no other technology. The process allows for fine-tuning critical attributes such as:
Particle Size and Morphology: Essential for ensuring proper drug absorption and bioavailability.
Moisture Content and Residual Solvent: Crucial for product stability and shelf life.
Density and Flowability: Influences downstream processes such as tableting or capsule filling.
Spray drying is especially beneficial for creating amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs), which are used to enhance the solubility and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. The process enables precise manipulation of these properties, helping to ensure high-quality, stable formulations.
How Spray Drying Works in Pharmaceutical Production
Pharmaceutical spray dryers vary in design based on factors such as the type of drying gas used, the atomization method, and the powder recovery system. Some key components include:
Drying Gas: Nitrogen is often preferred over air in pharmaceutical applications, as it helps prevent oxidation of sensitive compounds and is safer for drying organic solvents.
Atomizers/Nozzles: The choice of nozzle—whether pressure, two-fluid, or ultrasonic—affects the particle size and distribution of the final powder. Pressure and two-fluid nozzles are widely used for their ability to generate fine, consistent powders that flow easily during tablet or capsule filling.
Powder Recovery: Cyclones and filter bags ensure that only the desired product is recovered, leaving the drying gas behind.
Clean ability: Pharmaceutical spray dryers are designed with advanced clean-in-place (CIP) and sterilization-in-place (SIP) systems to prevent contamination and ensure product quality.
Applications in Pharma: Beyond Amorphous Solid Dispersions
Spray drying plays a pivotal role in creating inhalable drugs by forming fine powders with the ideal particle size distribution for efficient delivery to the lungs. Additionally, the process can encapsulate active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) within a protective matrix, enhancing drug stability and enabling controlled release.
In the production of amorphous solid dispersions (ASDs), closed-loop spray dryers using nitrogen as a drying gas are often employed to handle organic solvents and minimize oxidation risks. The precise control over particle size and morphology ensures these dispersions are effective in improving the solubility of poorly soluble drugs.
Key Advantages of Spray Drying in Pharma
Tailored Powder Properties: Spray drying allows for fine-tuning critical characteristics like particle size and morphology, ensuring the final product meets precise pharmaceutical specifications.
Cost-Effective: Compared to other drying methods like freeze drying, spray drying offers greater efficiency and lower costs, which is critical for scaling production in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Gentle Process: Spray drying is ideal for heat-sensitive materials like proteins or biologics, as the rapid drying process minimizes heat exposure, preserving product integrity.
Versatility: Spray drying can handle various feed types—solutions, suspensions, or emulsions—making it adaptable for a wide range of pharmaceutical applications, from small-molecule drugs to complex biologics.
Looking Ahead as the pharmaceutical industry moves toward more personalized and targeted treatments, spray drying is poised to become an even more integral part of drug production. The ability to tailor the properties of pharmaceutical powders, maintain high product quality, and improve process efficiency makes spray drying a key technology in the ongoing advancement of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
With continuous improvements in spray drying equipment and better modelling tools, the process is becoming more lean and risk-free, enabling quicker, more cost-effective scale-up and smoother transitions from research and development to commercial production.
As pharmaceutical manufacturing continues to evolve, spray drying is proving to be an indispensable technology—delivering precision, flexibility, and efficiency. With its ability to create powders with well-defined properties, it is clear that spray drying will remain a cornerstone of drug formulation and production for years to come.